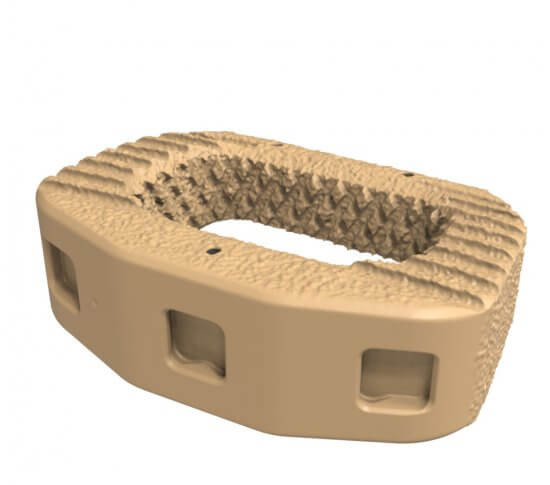
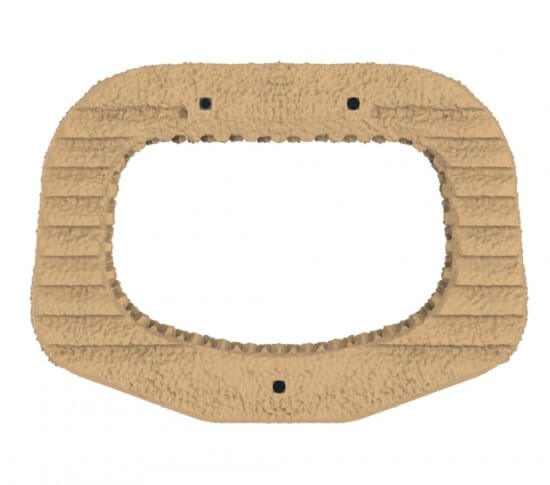
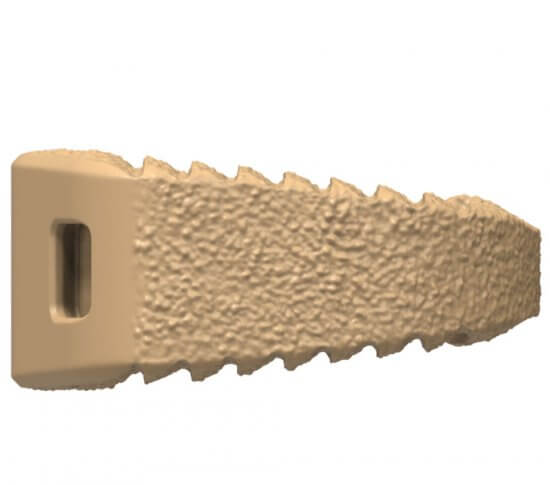
Fortilink®-A IBF System with TETRAfuse® 3D Technology
Adding to the TETRAfuse 3D Technology family of products, Fortilink-A with TETRAfuse 3D Technology offers patients a device designed to participate in the fusion process,¹† while maintaining bone-like mechanical properties1,††. The unique features of the 3D printed nano-rough surface have shown to allow bone cells to attach to the implant 1, increasing potential for fusion in an anterior spine fusion surgery.
Regulatory approvals vary by country. Therefore, we kindly ask you to contact the distributor in your region regarding availability of specific products, implants and / or instrumentation in your region.